What is difference between shielded and unshielded cable?
Published:
2024-03-18 04:03:55
Shielded cables are versatile in terms of compatibility with different networking technologies.
In the world of cable technology, two prominent types of cables coexist: shielded cables and unshielded cables. These cables differ significantly in terms of construction, purpose, and effectiveness. From shielding wires to electrical interference, understanding the dissimilarities between shielded and unshielded cables is essential for choosing the right option for specific applications.
1. Construction and Composition
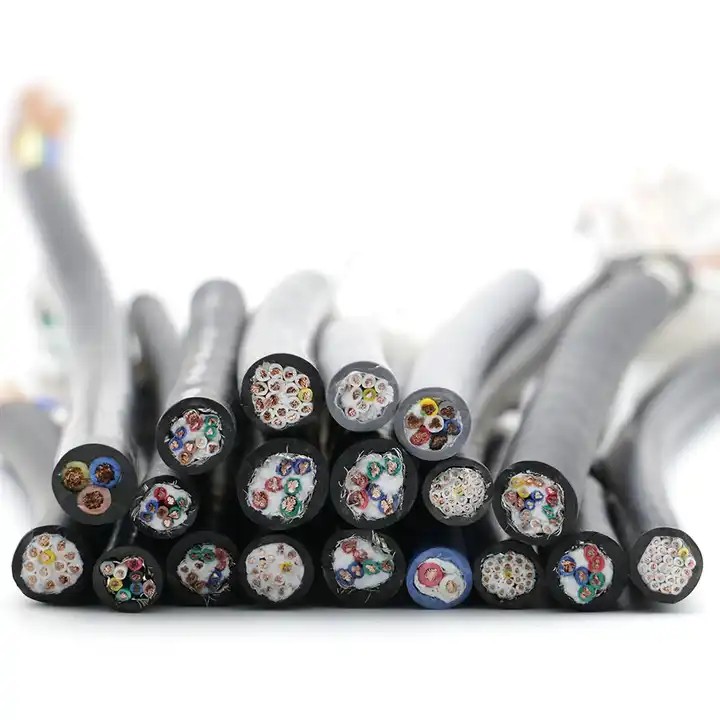
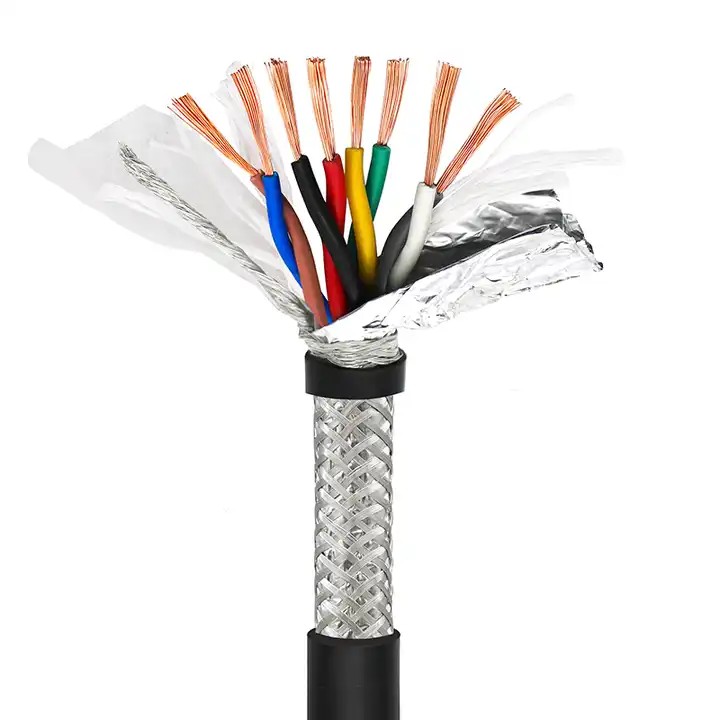
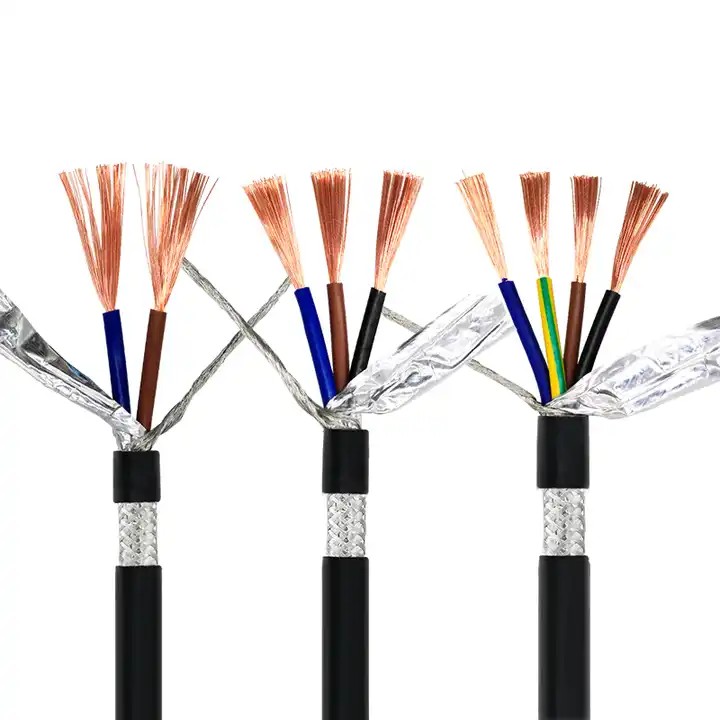
Shielded cables, also known as screened cables, are manufactured with an additional layer of shielding material. This shielding layer consists of metal or conductive materials, usually aluminum or copper. The shielding encloses the conductors inside and provides an extra level of defense against external electromagnetic interference.
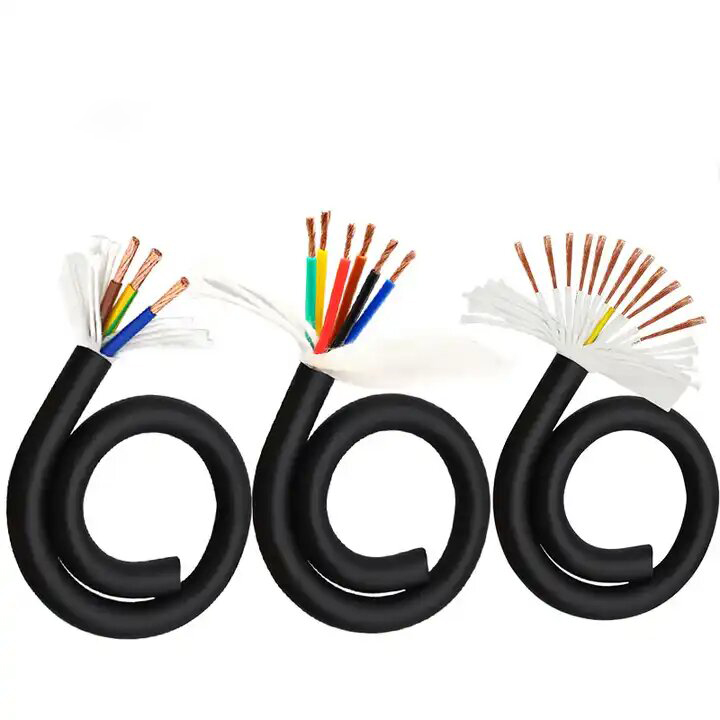
On the other hand, unshielded cables, often referred to as unscreened cables or UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables, lack the protective shielding layer seen in shielded cables. These cables usually consist of multiple pairs of twisted copper wires, with each pair individually insulated.
2. Intended Applications
Shielded cables are primarily used in environments prone to high levels of electrical noise interference. These cables are beneficial in settings like manufacturing plants, computer networking, telecom installations, and hospitals where protection against electromagnetic interference (EMI) is critical. Shielded cables ensure signal integrity by minimizing cross-talk and enhancing overall performance.
Unshielded cables are commonly used in applications where EMI is less of a concern, such as residential installations. Due to their cost-effectiveness and simplicity, unshielded cables find extensive use in Ethernet connections, telephone lines, and home networking.
3. Protection against Electrical Interference
The primary purpose of shielded cables is to protect against various forms of electrical interference. The shielding layer effectively mitigates both electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). Shielded cables are capable of maintaining signal strength by preventing external disruptions from distorting or weakening the transmitted data.
Unshielded cables, however, are susceptible to interference, which can lead to signal degradation. This interference can affect the data transmission quality, resulting in errors, loss of efficiency, and reduced data transfer rates. Despite their vulnerability to interference, unshielded cables are commonly used in short-range applications with minimal electrical noise.
4. Installation and Cost
Installing shielded cables can be more complex compared to unshielded cables due to the added layer of shielding. Shielded cables often require proper grounding to effectively eliminate electrical noise. Additionally, specialized connectors and equipment may be necessary, leading to higher installation costs.
In contrast, unshielded cables are relatively simple to install. They do not require grounding and can be terminated using standard connectors, making the installation process hassle-free and cost-effective.
5. Performance and Bandwidth
Shielded cables offer superior performance in terms of reducing noise and providing higher bandwidth capabilities. They provide enhanced signal integrity, allowing for longer transmission distances without signal degradation. The shielding helps maintain the data integrity, making shielded cables ideal for critical applications that require high-speed and reliable data transfer.
Unshielded cables, while not providing the same level of protection, can still deliver satisfactory performance for regular data transmission needs. They are suitable for short to medium-range connections and offer sufficient bandwidth for typical residential or office requirements.
6. Versatility
Shielded cables are versatile in terms of compatibility with different networking technologies. They can support various protocols like Ethernet, Fibre Channel, and Token Ring. Shielded cables are available in different categories, such as STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) and FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair), allowing flexibility in meeting specific requirements.
Unshielded cables, particularly UTP cables, are widely used for Ethernet connections and are compatible with numerous networking standards. However, they may not be suitable for certain applications that demand high levels of electrical noise protection.
In summary, the choice between shielded and unshielded cables depends on the specific application requirements and the level of electrical noise protection needed. Shielded cables provide superior protection against interference and excel in critical settings where signal integrity and performance are paramount. Unshielded cables offer cost-effectiveness and simplicity for less demanding applications. By understanding their differences and characteristics, one can confidently select the appropriate cable type for optimal performance and reliability.