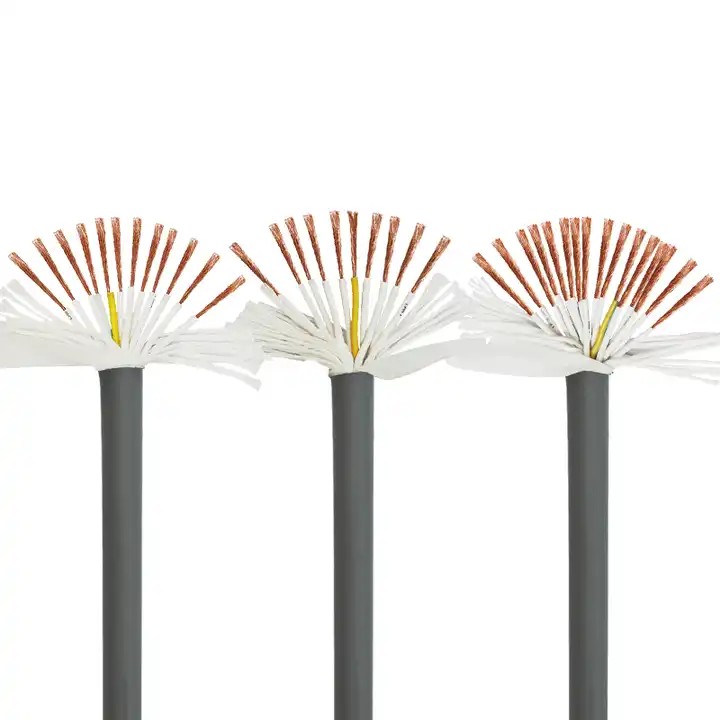
Why Is Shielding Necessary for Electrical Wires and Cables?
Published:
2024-09-12 16:37:19
Explore high-quality shielded power cables designed to enhance performance and safety in various applications. Discover reliable shielded Ethernet cables for superior data transmission and network security. Find trusted shielded power cable suppliers offering a range of solutions to meet your specific needs.
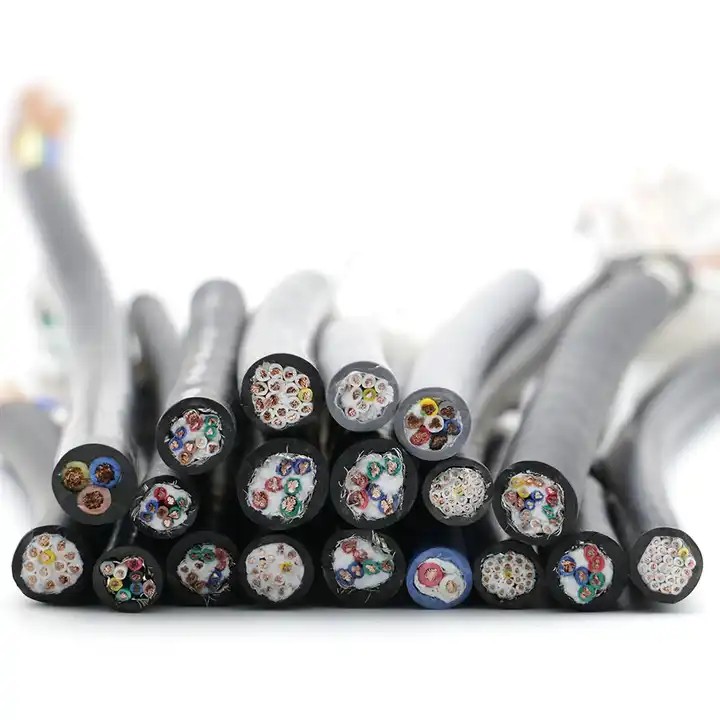
When current flows through a conductor, it generates a magnetic field around it, producing substantial electromagnetic signals. Shielding power cable involves creating a metallic barrier between two spatial areas, serving as an electromagnetic isolation layer. Essentially, it is a method to improve the dispersion of electrostatic fields.The degree of shielding required for wires and cables depends on several factors: the electrical environment in which the cables are used, the cost of the cables, the diameter of the conductors, weight, and flexibility.
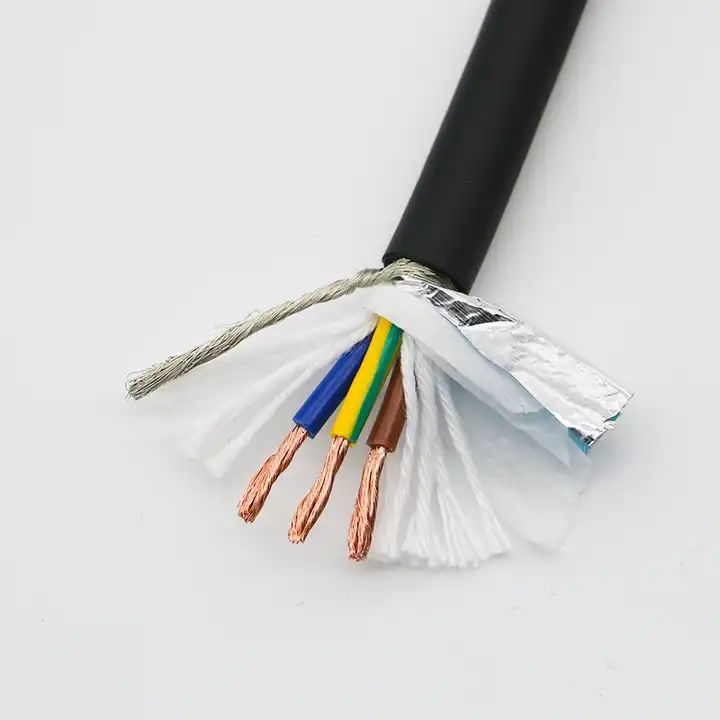

Here are the primary reasons for using shielding:
Ensuring Transmission Performance in Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) Environments: Shielding protects against external electromagnetic interference and reduces the system's own electromagnetic emissions. Effective shielding minimizes disruptions and ensures reliable data transmission.
Providing Grounding Protection: In case of conductor damage, the shielding allows leakage current to safely flow into the grounding network, preventing electrical hazards and improving safety.
Key Applications of Shielded Cables
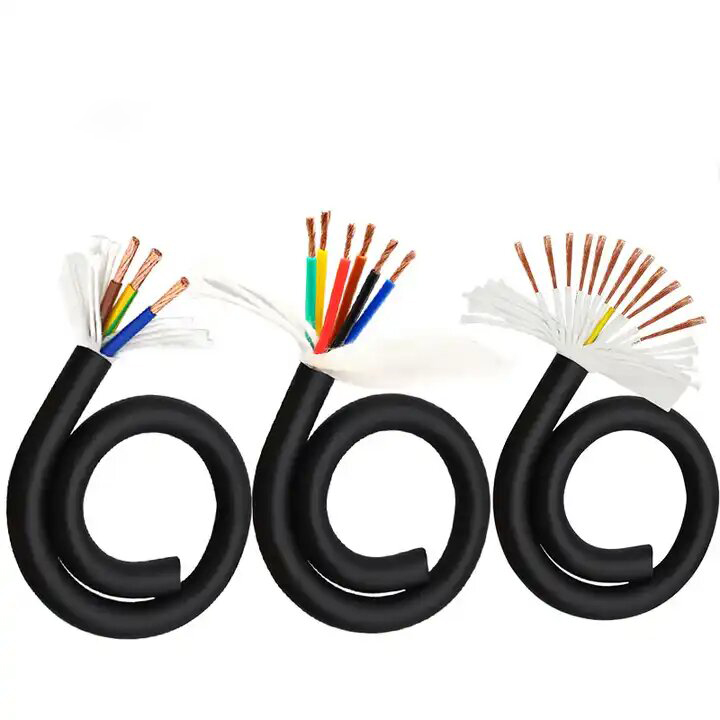
Signal Transmission Scenarios: Shielded cables are essential for scenarios requiring signal transmission, such as data cables, network cables, audio cables, and video cables.
Industrial Automation: These include motor connection cables, frequency converters, and servo drive cables. Adjustments to the sheath material and braid density can enhance suitability for drag chains and other demanding environments.
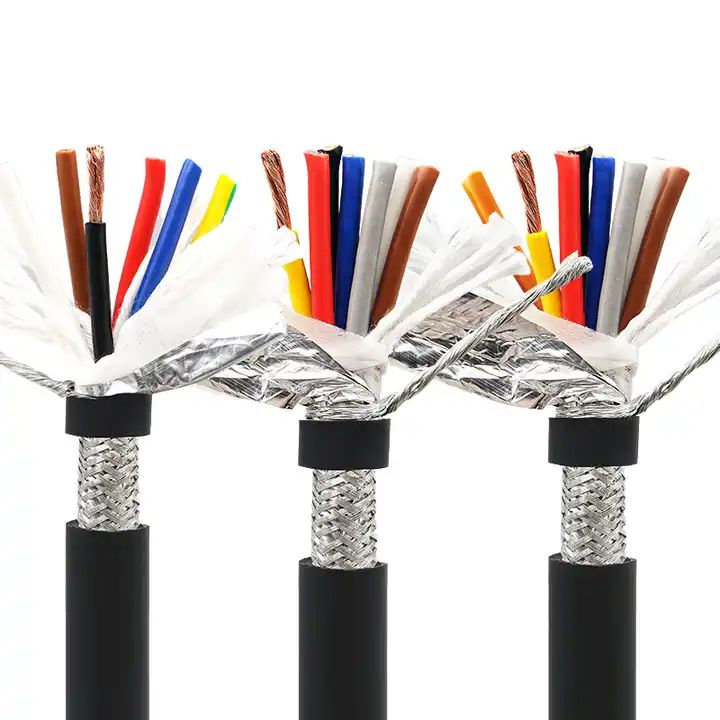

Types of Shielding and Material Choices
1. Metal Foil Shielding:
Metal foil shielding, typically made of aluminum or copper foil, involves applying a thin layer of foil around the conductor. This type of shielding offers 100% coverage around the conductor, enhancing strength and durability.
Aluminum Foil Shielding: Often used with one conductive side and one insulating side. The conductive side (usually silver) ensures effective shielding, while the insulating side (often blue) helps in distinguishing the foil during production. In double-layer shielding, the conductive side faces outward, closely contacting the braided layer for tighter shielding. In single-layer shielding, the conductive side connects to the ground, ensuring complete coverage.
Color-Coded Foil: For example, HDMI cables use different colored foils to differentiate between cores.
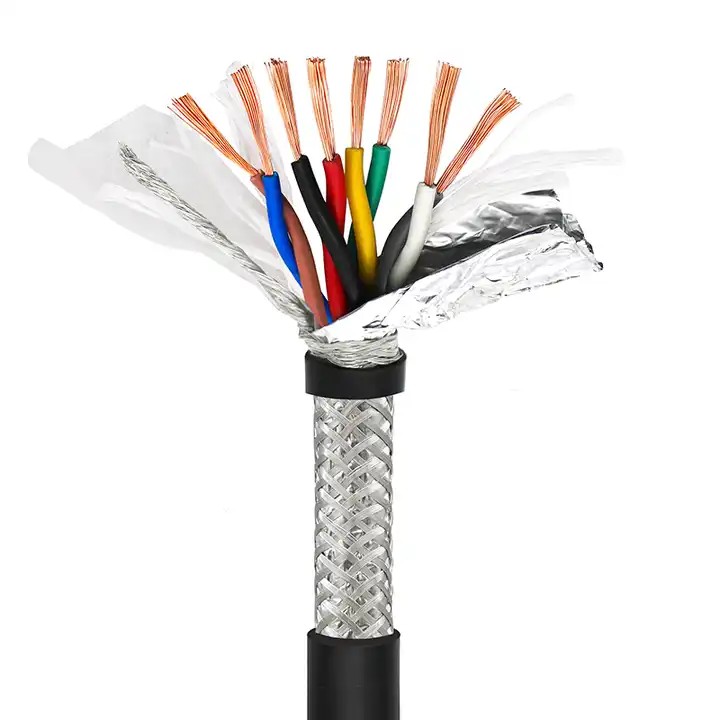
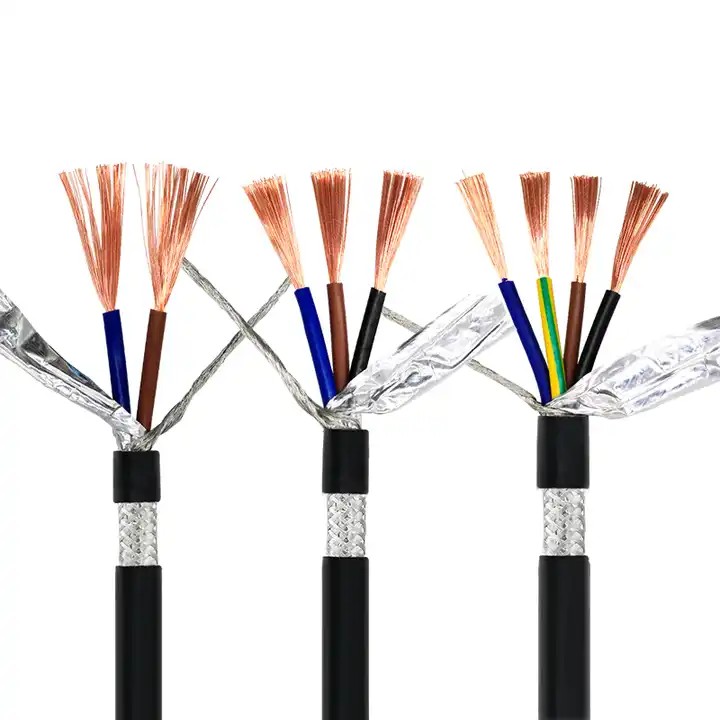
2. Metal Braid Shielding:
Metal braid shielding involves wrapping the shielded ethernet cable with a woven mesh of non-magnetic metals like copper or aluminum. While braid shielding provides a low-resistance path to ground and is easier to attach or weld, it does not offer 100% coverage.
- Material Choices:
- Pure Copper: Offers excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and durability.
- Tin-Plated Copper: More resistant to oxidation and corrosion than bare copper, with improved solderability and reliability, though it is generally more expensive.
- Aluminum-Magnesium Alloy: Lightweight and cost-effective, suitable for applications where high performance is less critical.
Select the appropriate cable shielding material based on the specific requirements of your product. Each type of shielding and material offers distinct advantages tailored to different applications, balancing factors such as performance, cost, and environmental conditions.