Testing and verifying the performance of shielded twisted pair (STP) cables is a crucial process to ensure the reliability and integrity of data transmission in network infrastructures. Shielded twisted pair cables are used extensively in various applications, including Ethernet networks, telecommunication lines, and other signal transmission systems where electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) are concerns. Here’s a detailed guide on how to test and verify the performance of STP cables:
1. Understanding Shielded Twisted Pair Cables
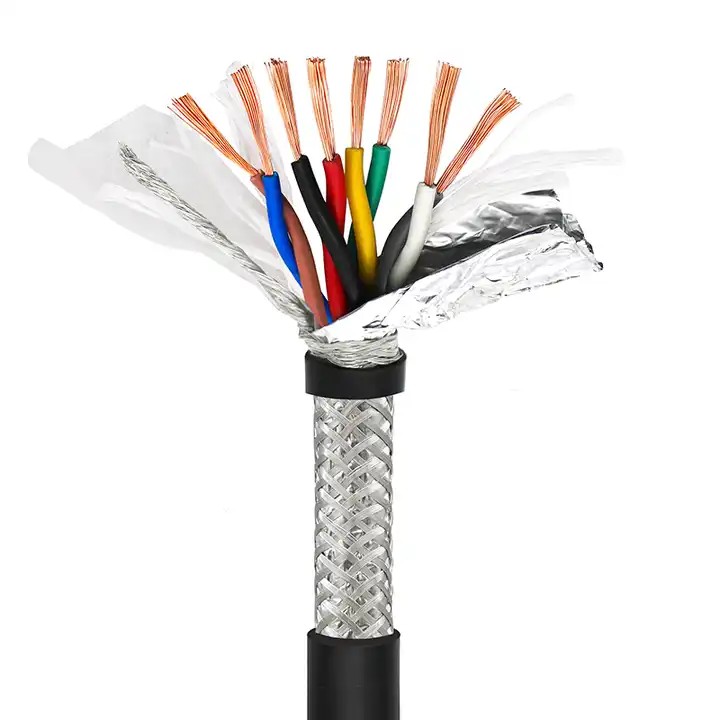
Before testing, it’s important to understand the structure of STP cables. They consist of pairs of insulated conductors twisted around each other, which helps to reduce crosstalk and electromagnetic interference. The entire assembly is enclosed in a shielding layer, typically made of foil or braided metal, to further protect against external interference.
2. Visual Inspection
The first step in testing is a thorough visual inspection. Check for any physical damage, such as cuts, kinks, or abrasions that could affect the cable’s performance. Ensure that the connectors are securely attached and free from corrosion.
3. Continuity Testing
Continuity testing is essential to verify that there are no breaks in the cable. This can be done using a multimeter or a time domain reflectometer (TDR). A TDR sends a signal down the cable and measures the time it takes for the signal to return after hitting an impedance mismatch, indicating a break or a connector.

4. Wire Map Testing
Wire map testing checks the correct pairing of the wires within the cable. This is important because improper wiring can lead to signal integrity issues. A wire map tester can identify any reversals or swaps in the wire pairs.
5. Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates the cable's ability to transmit signals without significant loss or distortion. This includes:
- Attenuation Test: Measures the reduction in signal strength as it travels along the cable.
- Return Loss Test: Determines how much of the signal is reflected back due to impedance mismatches.
- Insertion Loss Test: Measures the total loss in dB from the input to the output of the cable.
6. Near-End Crosstalk (NEXT) Testing
NEXT testing assesses the interference caused by signals from adjacent pairs within the same cable. This is critical for ensuring that the cable meets the required standards for data transmission, especially in high-density environments.

7. External Influence Testing
Since STP cables are designed to resist external interference, it’s important to test their shielding effectiveness. This can involve exposing the cable to various sources of EMI and RFI to see how well it maintains signal integrity.
8. Cable Certification
Cable certification is a comprehensive testing process that verifies the cable meets industry standards for performance. It includes all the tests mentioned above and provides a detailed report on the cable’s performance.

Testing and verifying the performance of shielded twisted pair cables is a multi-step process that involves visual inspection, continuity testing, wire map testing, performance testing, NEXT testing, external influence testing, and cable certification. By following these steps, you can ensure that your STP cables are reliable and capable of supporting high-quality data transmission. Regular testing and documentation are key to maintaining the integrity of your network infrastructure.